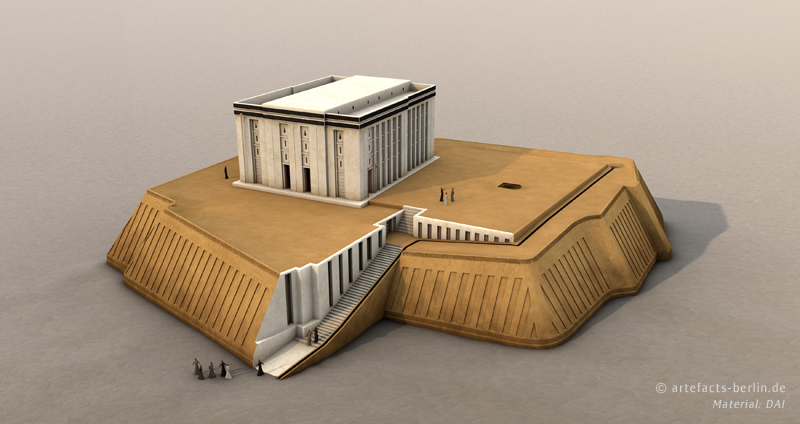
The “White Temple” of Uruk dates into the 4th mill. BCE and was visualized on behalf of the German Archaeological Institute by Artefacts Berlin.
A Uruk/Warka, situated in modern-day Iraq, is one of the first cities in the world and was populated almost without interruption for over 5,000 years. In the western area of the city centre a multiple-phased terrace was discovered, the so-called “Anu Ziggurat”. The terrace was extended and raised over time at least ten times until it reached a height of about 12 m.
This last construction level featured a polygonal shape, due to its many reconfigurations, sloped outer walls as well as a complicated staircase. The surface area of the terrace measured about 45 x 50 m. The remains of an elaborated middle-hall-building, the so-called “White Temple”, were found on top of the terrace. The building had white plastered walls, which were divided by niches, multiple postaments, maybe shelves in an adjacent room as well as multiple staircases, which led to the roof or to a second storey. The erection of the building was radiocarbon-dated between 3517 and 3358 BCE.
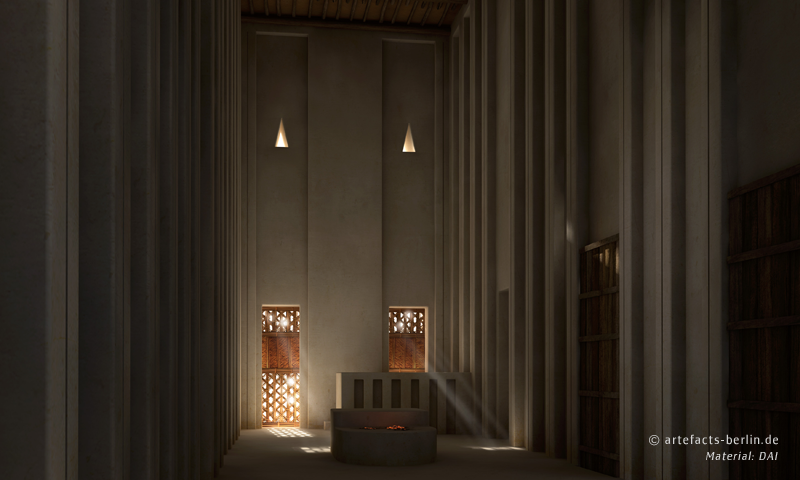

In the process of the reconstruction the team of Artefacts Berlin decided for two alternatives: a one-storey and a two-storey version. The reconstructions are based on the excavation results, but also on a small temple model made from stone that was found in a corner of the “White Temple” during the excavation. The proportions and wall decorations of the reconstruction were adopted from this model which had nearly the same ground plan as the actual building.
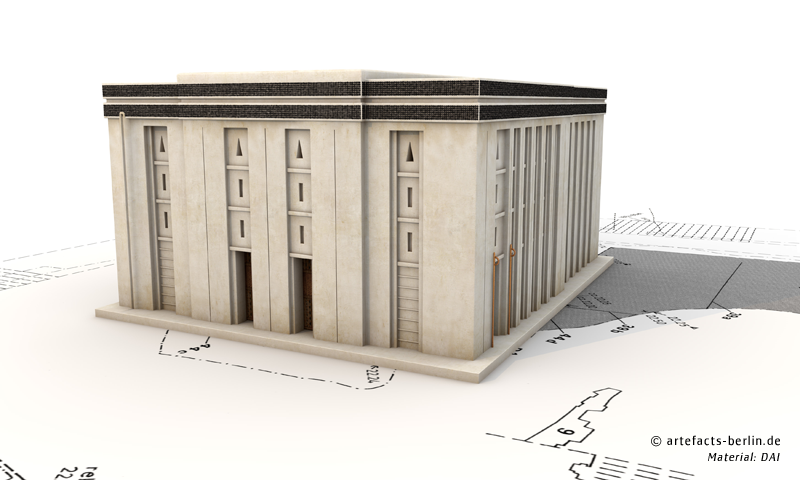
Source: Artefacts Berlin
Image: General view on the “White Temple” | © artefacts-berlin